Die Erosion
Defects
Die erosion, cavitation, and burn out are defects that can occur in castings when the die has worn spots, causing raised spots on the casting. These defects can also be caused by small deep cavities (cavitation) or larger erosion areas at the gate.
Cause
The cause of die erosion, cavitation, and burn out can be high metal velocity, bubbles in incoming metal, or high oxide or silicon content in metal.
Corrections
- Check gate velocities:
- Aluminum metal velocities should be about 1000 ips to 16000 ips
- For zinc, gate velocity should be about 1200 ips to 2000 ips
- For magnesium, gate velocity should be about 1200 ips to 3000 ips
- Check metal temperature: It should not be high.
- Check die temperature in the gate area: Reduce with spray if possible.
- Check metal cleanliness: Oxide cleaning procedures should be in place.
- Check fill times: Long fill times accelerate gate erosion.
- Check alloy: Hyper-eutectic (high silicon) alloys require smaller process window (lower gate velocities).
- In zinc: Trapped air bubbles cause cavitation and burn out.
- Check gate design: Small design mistakes can cause cavitation.
- Change gate locations: Try to find a location where the gate doesn't impinge on die steel.
- Use slow shot speed on plunger to reduce trapped gases: Set it so the plunger moves slowly up to the sprue.
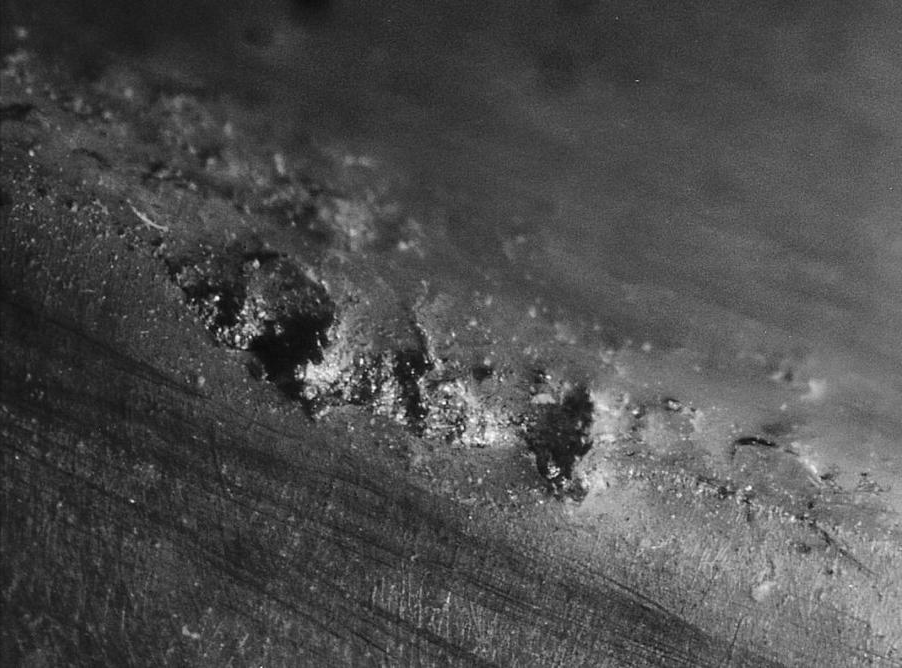
Cavitation (10X).
Please note that the information provided in this article is intended to be a general guide to the causes and corrections of die erosion. However, it is important to note that the specific cause and correction of any particular defect will vary depending on the specific casting process, alloy, and other factors. Therefore, it is important to consult with an experienced and professional engineer to ensure that the correct diagnosis is made and the most suitable correction is chosen.