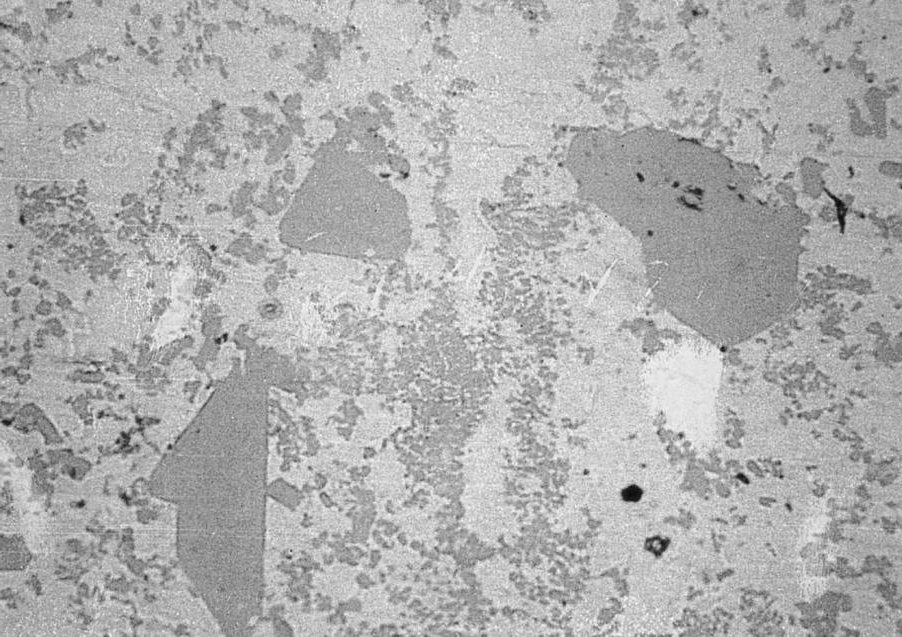
Inclusions Defect
Defects
Cause
In aluminum, inclusions are often oxides caused by poor melt-cleaning and furnace cleaning practices. They can also be caused by furnace refractory. Iron aluminum inter-metallics in zinc alloys can lead to polishing and machining problems.
Corrections
- Aluminum: Inclusions are probably formed in the melting furnace. Check cleaning procedures:
- Examine the melt line and corners for build-up.
- Scrape the bottom of the furnace for excessive corundum material.
- Check wall cleaning procedures:
- Use the proper tools.
- Make sure operators are trained.
- Maintain the cleaning schedule.
- Allow at least half an hour between cleaning and delivering metal. More is better.
- Check fluxing procedures. Flux once per shift.
- Check de-gassing procedures. Do this as often as possible.
- Check the filter system:
- Replace filters as needed.
- Make sure filters aren't leaking around the edges.
- Review the temperature at central melting. Is it too high? (730-760°C is best.) Use one setting; do not allow variations.
- Check holding furnaces for oxide build-up and cleaning procedures:
- Does the temperature vary too much? (Look for high temperature swings.)
- Hard spots (or hard areas) may contain sludge. Check the bottom of the furnaces and review the holding furnace temperatures for sludge.
- Some hard spots are refractory material. This can be caused by cleaning and then tapping the furnace too soon.
- For zinc and ZA alloys, reduce hot spots in the pot and reduce excessive fluctuations in furnace temperature.
- Most of the harder material will rise to the surface as dross and can be skimmed off (if allowed to form).
- For ZA alloys, keep the iron content below 0.75%.
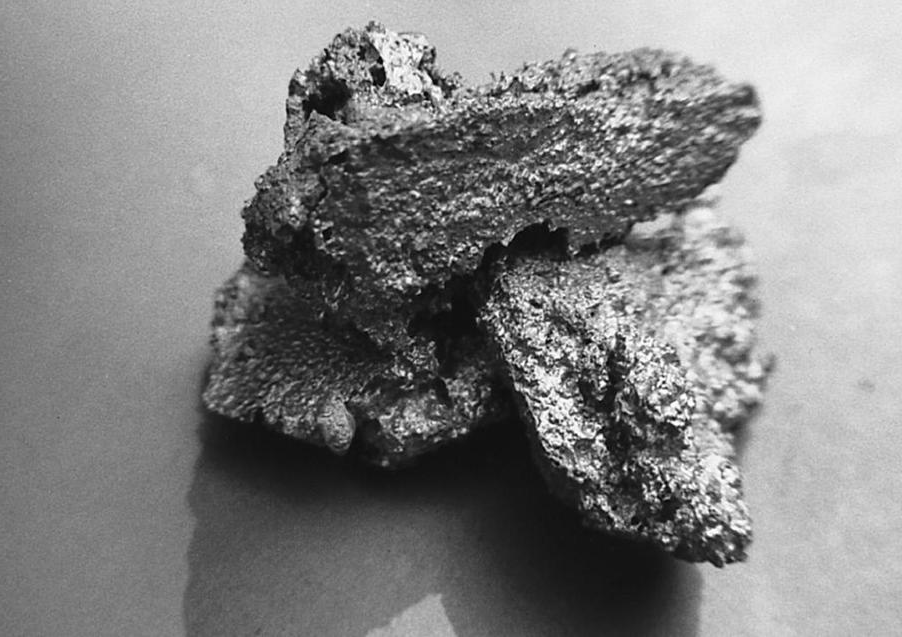

Please note that the information provided in this article is intended to be a general guide to the causes and corrections of inclusions defects in metal castings. However, it is important to note that the specific cause and correction of any particular defect will vary depending on the specific casting process, alloy, and other factors. Therefore, it is important to consult with an experienced and professional engineer to ensure that the correct diagnosis is made and the most suitable correction is chosen.